Therefore, these have to be spread evenly across products in the case where the company is a manufacturing concern and produces a single product. Instead, it will divide the cost of the building by a small whole number such as 3 or 5 and expense the building by that fraction over the next 3 or 5 years. The reason they do this is to avoid showing a very poor financial performance in one period when the value of the building lasts many years. Comprehensive Problem LO3-1, LO3-2, LO3-4Gold Nest Company of Guandong, China, is a family-owned enterprise that makes birdcages for the South China market.
Ongoing Overapplied Overhead
Indirect labor employees and workers assist direct labor employees and workers in their work and handle the day-to-day tasks that are essential to running a business. The roles that indirect labor employees perform range from financial duties, such as bookkeeping and budgeting, to tasks like equipment maintenance and appliance repair. Based on these two journal entries, the balance in the labor cost account should be zero at the end of the period.

Direct cost Vs. Indirect Cost – What are the Key Difference?
- Managers use the information in the manufacturing overhead account to estimate the overhead for the next fiscal period.
- In order to respond quickly to production needs, companies need raw materials inventory on hand.
- The job cost accounting journal entries below act as a quick reference, and set out the most commonly encountered situations when dealing with the double entry posting of job costing.
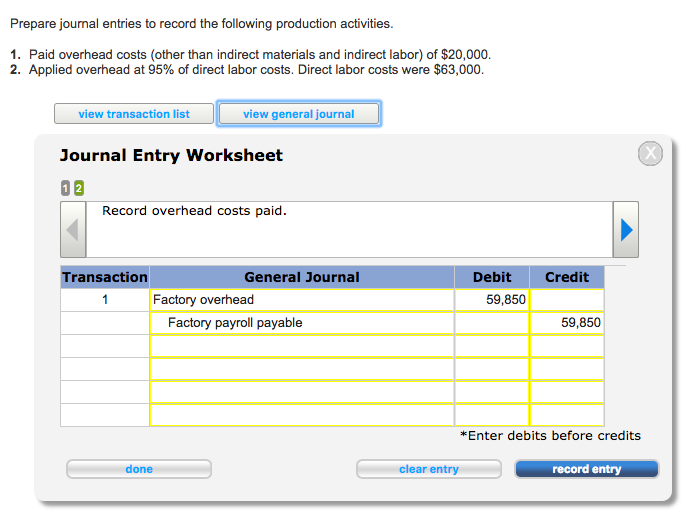
- As the overhead costs are actually incurred, the Factory Overhead account is debited, and logically offsetting accounts are credited.
- Sometimes the company learns that certain jobs are too costly considering the prices they can charge.
On the other hand, printing instruction manuals was quite profitable, so the company has focused more on the instruction manual market. To illustrate a job costing system, this section pnl explained faq describes the transactions for the month of July for Creative Printers. The company compares the cost of each job withthe revenue received to be sure the jobs are profitable.
Conceptual Journey of Inventory & Wages Across Financial Statements
Moreover, the interface boasts an intuitive design and the entire system is very user-friendly. The production department employees work on the sign and send it over to the finishing/assembly department when they have completed their portion of the job. Direct Labor Costs are costs that are incurred during the manufacturing process, and therefore, these costs can also be directly traceable and attributable to a given product. Indirect Labor Costs can be defined as costs that cannot be directly traced to an individual product.
Accounting For Actual And Applied Overhead
If the actual is less than the applied overhead, they may ask the accountants to reduce the overhead applied to jobs. The total job cost of Job 106 is $27,950 for the total work done on the job, including costs in beginning Work in Process Inventory on July 1 and costs added during July. This entry records the completion of Job 106 by moving the total cost FROM work in process inventory TO finished goods inventory. The company compares the cost of each job with the revenue received to be sure the jobs are profitable. Sometimes the company learns that certain jobs are too costly considering the prices they can charge. For example, Creative Printers recently learned that cookbooks were not profitable.
In addition to basic wages and salaries, an entity’s direct labor cost includes all costs and expenses needed to hire and keep direct labor workers in the organization. These costs and expenses take the form of relevant federal and state taxes, contributions and benefits provided by employers for the support and wellness of workers. Due to this reason, an entity’s total direct labor cost is often much higher than just the basic production related wages or salaries paid to workers as their remunerations. In this journal entry, the labor cost account includes both direct labor and indirect labor. And the payroll taxes payable account is a current liability account that the company owes to the applicable governing authorities.
When both administrative and production activities occur in a common building, the production and period costs would be allocated in some predetermined manner. These costs are necessary for production but not efficient to assign to individual product production. Examples of typical overhead costs are production facility electricity, warehouse rent, and depreciation of equipment. For example, employees may fill out time tickets that include job numbers and time per job, or workers may scan bar codes of specific jobs when they begin a job task. Please note that in the employee time tickets that are displayed, each employee worked on more than one job. Indirect labor is a category of indirect cost and refers to those employees that assist the direct labor in the performance of their work.
To understand capitalized expenses, you need to know what depreciation and amortization are. When a company buys a big asset, such as a building, it doesn’t include the cost of the building in one period on the profit and loss statement. The salaries of certain employees such as hourly-paid administrative assistant may be variable i.e. they may increase or decrease during certain times in a year.
The materials are sent to the production department as it is needed for production of the products. Like direct labor, a significant part of total indirect labor cost consists of fringe benefits, employer’s contributions and payroll taxes etc. Any expense or cost caused by non-production workers like office, administrative or security personnel etc. can’t be regarded as direct labor cost.
Then, these costs including the $20,000 of indirect labor will be transferred further to the working in process account using the predetermined overhead rates. In traditional costing systems, the most common activities used as cost drivers are direct labor in dollars, direct labor in hours, or machine hours. Often in the production process, there is a correlation between an increase in the amount of direct labor used and an increase in the amount of manufacturing overhead incurred. If the company can demonstrate such a relationship, they then often allocate overhead based on a formula that reflects this relationship, such as the upcoming equation. While many types of production processes could be demonstrated, let’s consider an example in which a contractor is building a home for a client. The accounting system will track direct materials, such as lumber, and direct labor, such as the wages paid to the carpenters constructing the home.



